Molecular mechanism of mitochondrial phosphatidate transfer by Ups1
(In collaboration with Prof. Jun Fan, City University of HongKong)
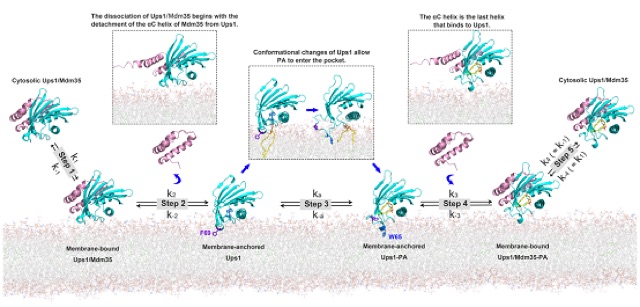
A working model for Ups1/Mdm35-mediated PA transport.Step 1. Ups1/Mdm35 interacts with the membrane via the membrane-binding residues of Ups1. Step 2. the dissociation of Mdm35 from Ups1 leads to membrane insertion of F69. anchoring Ups1 into the membrane. Step 3. PA-binding results in a conformational change in Ups1. where W65 is inserted in the membrane instead of F69. Step 4. Mdm35 binds to Ups1 PA. Step 5. Ups1 PA/Mdm35 is released from the membrane to the aqueous environment.
Cardiolipin, an essential mitochondrial physiological regulator, is synthesized from phosphatidic acid (PA) in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). PA is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and transferred to the IMM via the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) under mediation by the Ups1/Mdm35 protein family. Despite the availability of numerous crystal structures, the detailed mechanism underlying PA transfer between mitochondrial membranes remains unclear. Here, a model of Ups1/Mdm35-membrane interaction is established using combined crystallographic data, all-atom molecular dynamics simulations, extensive structural comparisons, and biophysical assays. The α2-loop, L2-loop, and α3 helix of Ups1 mediate membrane interactions. Moreover, non-complexed Ups1 on membranes is found to be a key transition state for PA transfer. The membrane-bound non-complexed Ups1/ membrane-bound Ups1 ratio, which can be regulated by environmental pH, is inversely correlated with the PA transfer activity of Ups1/Mdm35. These results demonstrate a new model of the fine conformational changes of Ups1/Mdm35 during PA transfer.
Reference:
Lu J.#, Chan C.#, Yu L.#, Fan J.*, Sun F.* and Zhai Y.* (2020) Molecular mechanism of mitochondrial phosphatidate transfer by Ups1. Communications Biology, 3: 468. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01121-x
附件下载: