Cryo-EM structure of the plant actin filaments from Zea mays pollen
(In collaboration with Prof. Haiyun Ren from Beijing Normal University)
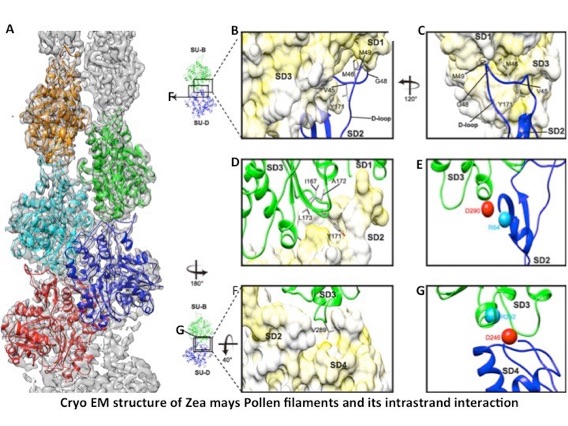
The actin cytoskeleton plays vital roles in many fundamental processes ranging from vesicle and organelle transportation, endo- and exocytosis to cell division and growth. Actin exists as two states in vivo, actin monomers (G-actin) and actin filaments (F-actin), which are subject to a dynamic equilibrium of polymerization and de-polymerization. In most instances, F-actin is the functional form of actin proteins. Thus, studying the structure of F-actin is of particular importance for understanding its functional mechanism. Recently, the evolution of cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) technology has enabled the determination of high resolution filamentous structures of rabbit skeleton muscle actin (RSMA) in different nucleotide states as well as the jasplakinolide-stabilized malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum actin 1 (JASP-PfAct1). Despite high protein sequence identity between plant and animal actins, their biochemical activities as well as cellular functions are different. However, the structural basis accounting for these differences remains poorly understood, largely because none of the plant F-actin structures has been resolved.
In this work, we get a 3.9 ? structure of the plant actin filament (ZMPA) from Zea mays pollen using cryo-electron microscopy. The structure shows a right-handed, parallel and staggered architecture that is stabilized by intra- and inter-strand interactions. Whilst the overall structure resembles that of other actin filaments, its DNase I-binding loop (D-loop) bends further outward, which adopts an open conformation similar to the jasplakinolide-stabilized mammalian actin filament. Therefore, our structural data give insights into how plant actin filaments have enhanced stability when compared with animal actin filaments, which is important for their roles as tracks for long-distance vesicle and organelle transportations.
Reference:
Ren Z., Zhang Y., Zhang Y., He Y., Du P., Wang Z., Sun F.* and Ren H.* (2019) Cryo-EM structure of actin filaments from Zea mays pollen. Plant Cell. pii: tpc.00973.2018. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00973.
附件下载: