神经性疼痛(neuropathic pain,NP)是由外周或中枢躯体感觉系统的损伤或疾病导致的疼痛,往往会引起刺痛或烧灼感,也有可能对触摸或寒冷敏感[1]。神经性疼痛的全球发病率约为7%~8%,给患者带来了巨大的经济或社会负担[2]。

针对神经性疼痛,临床上目前主要采取药物治疗,三环类抗抑郁药、加巴喷丁、普瑞巴林和5-羟色胺去甲肾上腺素再摄取抑制剂被推荐为一线药物[3]。但是,过量药物治疗往往会引起严重的副作用,或在可耐受剂量下仅提供了部分的疼痛缓解。而认知行为疗法(cognitive-behavioral therapy,CBT)、虚拟现实(virtual reality,VR)疗法等干预由于其无创、伤害小等特点越来越受到重视,逐渐成为疼痛治疗的替代疗法或补充疗法。
认知行为疗法
近年来,生物-心理-社会干预模式越来越受到重视,CBT被认为是治疗疼痛最常用的心理学方法。疼痛、情绪、认知、行为,以及社会环境之间是存在动态相互作用的。当我们的大脑充斥着消极的想法,比如"我做不到"、"我不如别人"等,就会引起焦虑不安的情绪,并做出相应的逃避行为。CBT就是在专业人员的帮助下,通过学习各种自我管理技能建立对疼痛的正确认知,通过放松训练或注意力转移训练来减少疼痛感知,从而改善慢性疼痛及相关的心理并发症[4-5]。
注意力转移是CBT中的常见疼痛应对技能。此外,研究发现,CBT干预使患者大脑神经网络连接发生改变,并且这种变化与情绪调节和认知功能改善相关(图1)。因此,CBT 可能通过情绪和认知管理调节脑区的神经环路改变,从而达到缓解认知功能障碍和减轻疼痛的目的。除了影响突触功能外,CBT还被证明可以抑制炎症因子IL-6的表达来缓解神经性疼痛[6]。
虚拟现实疗法
VR是一种基于交互性计算机的模拟技术,通过增强对用户视觉、听觉、触觉的反馈,使用户在虚拟环境中获得沉浸感和存在感[7]。该技术包括两大类:沉浸式和非沉浸式。沉浸式VR通常由头戴式显示器和3D输入设备组成,用户完全沉浸在与之交互的虚拟环境中。相反,非沉浸式VR使用户与真实世界环境保持某种感官联系[8]。VR将患者完全沉浸于虚拟的三维空间中,有助于减轻患者的焦虑、压力、恐惧和痛苦,从而帮助患者康复。
VR疗法包括虚拟行走、虚拟增强训练、虚拟错觉和虚拟催眠等,其中虚拟行走和经颅直流电刺激(transcranial direct current stimulation, tDCS)联合治疗被证明在缓解脊髓损伤相关的神经性疼痛中效果最明显[9]。VR疗法也可以根据用户类型,制定个性化的VR程序,如给予目标导向型训练,或者时间标记训练[10]。
各式各样的VR场景(海洋世界、丛林漫步等)可以将我们的注意力从疼痛短期转移,进而影响疼痛感知[11]。因此,3D头戴式VR比2D屏幕应用降低疼痛效果更好的可能原因是3D头戴式VR更能引起注意力转移。神经可塑性和神经环路及脑电的改变也是VR疗法干预神经性疼痛的重要机制。VR的使用可以增强视觉-听觉皮层激活,减少与初级躯体感觉皮层的功能连接,从而提高疼痛阈值[12]。此外,对慢性脑卒中患者进行基于沉浸式VR的运动控制训练干预,16周后血清IL-6水平下降17.96%,脑源性神经营养因子(brain derived neurotrophic factor,BDNF)浓度升高,这表明VR通过抑制炎症因子和神经可塑性等机制发挥作用[13]。
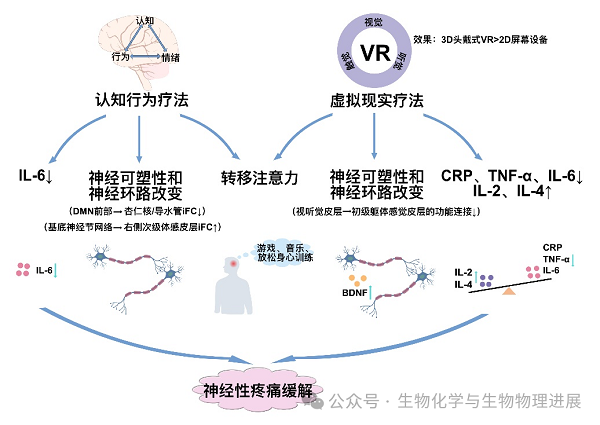
图1 认知行为疗法和虚拟现实疗法调控神经性疼痛机制
小结与展望
非药物的疼痛干预策略研究是当前疼痛研究者的关注热点,非药物的疼痛干预包括 CBT、VR、非侵入性的神经调控策略、积极干预疗法、运动干预等。CBT和VR疗法具有适用范围广,认知和行为相结合,受躯体功能障碍限制少的特点,两者联合使用或与药物治疗、其他非药物治疗联合使用可以作为新的有潜力的疼痛缓解方式。(详情请点击阅读原文)
参考文献
[1] Caragher S P,Khouri K S,Raasveld F V,et al. The peripheral nerve surgeon's role in the management of neuropathic pain. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open,2023,11(5):e5005
[2] Borgonetti V,Galeotti N. Rosmarinic acid reduces microglia senescence: a novel therapeutic approach for the management of neuropathic pain symptoms. Biomedicines,2022,10(7):1468
[3] Finnerup N B,Kuner R,Jensen T S. Neuropathic pain: from mechanisms to treatment. Physiol Rev,2021,101(1):259-301
[4] Saxena A K,Bhardwaj N,Chilkoti G T,et al. Modulation of mRNA expression of IL-6 and mTORC1 and efficacy and feasibility of an integrated approach encompassing cognitive behavioral therapy along with pregabalin for management of neuropathic pain in postherpetic neuralgia: a pilot study. Pain Med,2021,22(10):2276-2282
[5] Lumley M A,Schubiner H. Psychological therapy for centralized pain: an integrative assessment and treatment model. Psychosom Med,2019,81(2):114-124
[6] Saxena A K,Bhardwaj N,Chilkoti G T,et al. Modulation of mRNA expression of IL-6 and mTORC1 and efficacy and feasibility of an integrated approach encompassing cognitive behavioral therapy along with pregabalin for management of neuropathic pain in postherpetic neuralgia: a pilot study. Pain Med,2021,22(10):2276-2282
[7] Cassani R,Novak G S,Falk T H,et al. Virtual reality and non-invasive brain stimulation for rehabilitation applications: a systematic review. J Neuroeng Rehabil,2020,17(1):147
[8] Salatino A,Zavattaro C,Gammeri R,et al. Virtual reality rehabilitation for unilateral spatial neglect: a systematic review of immersive,semi-immersive and non-immersive techniques. Neurosci Biobehav Rev,2023,152: 105248
[9] Chi B,Chau B,Yeo E,et al. Virtual reality for spinal cord injury-associated neuropathic pain: systematic review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med,2019,62(1):49-57
[10] Lendaro E,Middleton A,Brown S,et al. Out of the clinic,into the home: the in-home use of phantom motor execution aided by machine learning and augmented reality for the treatment of phantom limb pain. J Pain Res,2020,13: 195-209
[11] Austin P D,Craig A,Middleton J W,et al. The short-term effects of head-mounted virtual-reality on neuropathic pain intensity in people with spinal cord injury pain: a randomised cross-over pilot study. Spinal Cord,2021,59(7):738-746
[12] Hu X-S,Beard K,Sherbel M C,et al. Brain mechanisms of virtual reality breathing versus traditional mindful breathing in pain modulation: observational functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. J Med Internet Res,2021,23(10):e27298
[13] Huang C Y,Chiang W C,Yeh Y C, et al. Effects of virtual reality-based motor control training on inflammation,oxidative stress,neuroplasticity and upper limb motor function in patients with chronic stroke: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Neurol,2022,22(1):21
作者简介
阮婷婷:宁波大学医学部研究生。研究方向为阿尔茨海默病的发病机制及干预。
徐淑君:宁波大学医学部教授。研究方向为阿尔茨海默病的发病机制及干预。
(作者:阮婷婷、徐淑君)
(本文来源于公众号:生物化学与生物物理进展)
 附件下载:
附件下载: